Heel Spur
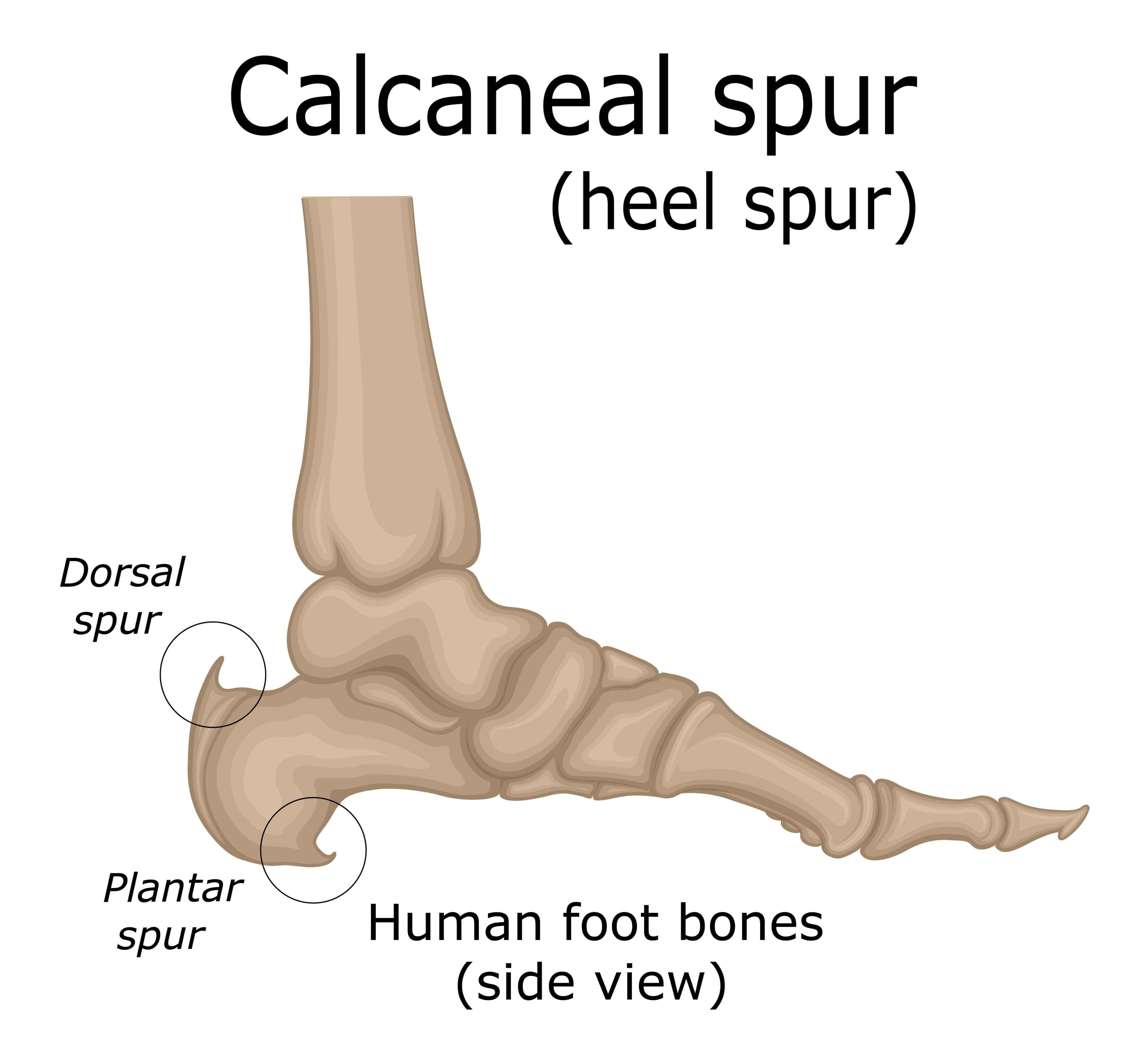
What are heel spurs, and what symptoms might indicate their presence?
Heel spurs are bony protrusions that develop on the underside of the heel bone. Often, individuals with heel spurs might not experience symptoms directly related to the spurs themselves. The pain associated with heel spurs generally arises from inflammation or irritation of the surrounding soft tissues, particularly the plantar fascia, causing a sharp pain in the heel or the bottom of the foot. Symptoms include localized pain, tenderness, and discomfort, especially when walking or standing for extended periods.
What causes heel spurs to develop?
Heel spurs typically develop in response to long-term strains or stresses on the plantar fascia, causing calcium deposits to form on the heel bone. Activities that repeatedly stress the heel or the fascia, such as running, jumping, or wearing poorly fitting shoes, can contribute to the development of heel spurs. Risk factors include age, biomechanical factors (like having flat feet or high arches), obesity, and certain occupations that involve prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces.
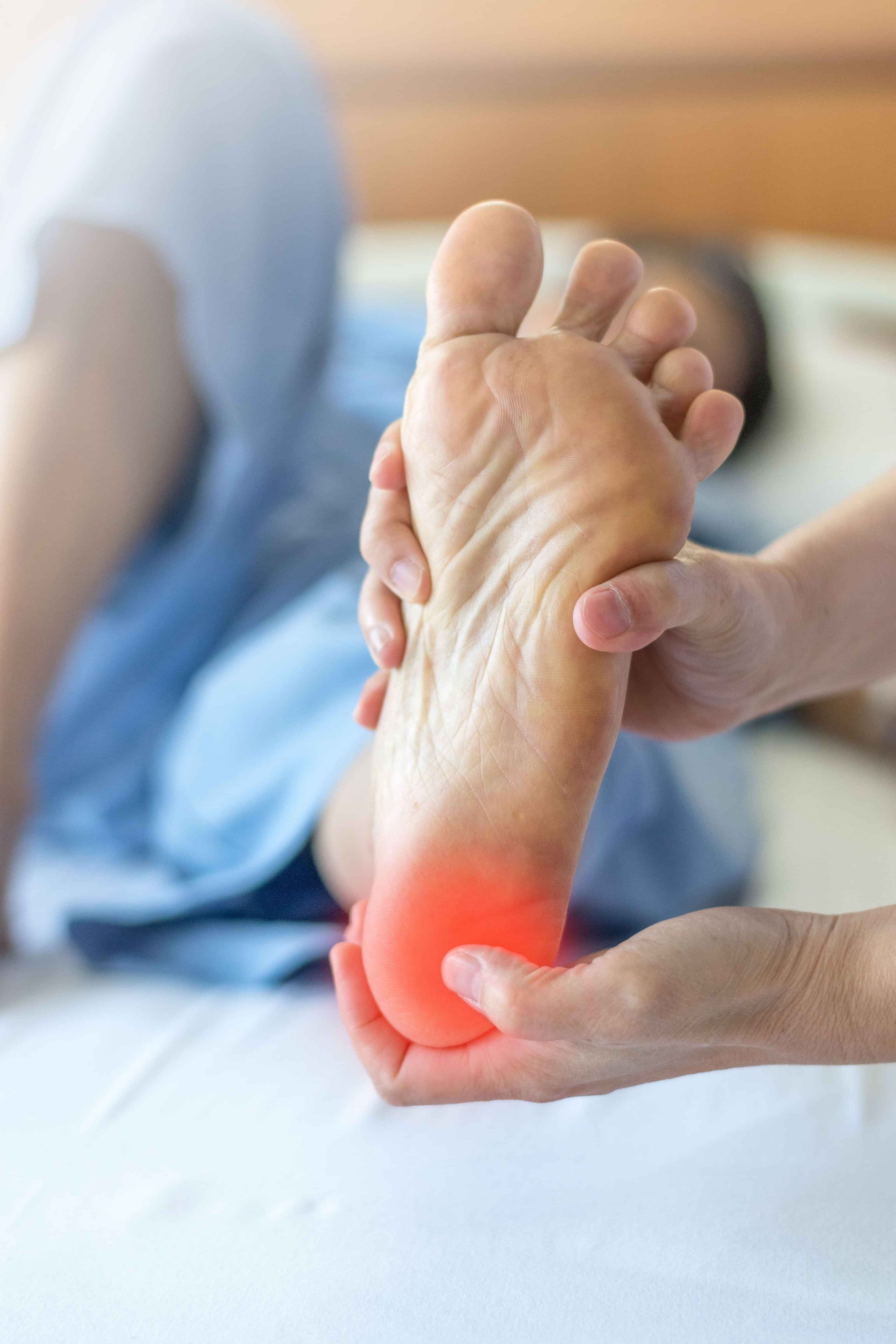
How are heel spurs diagnosed and differentiated from other conditions like plantar fasciitis?
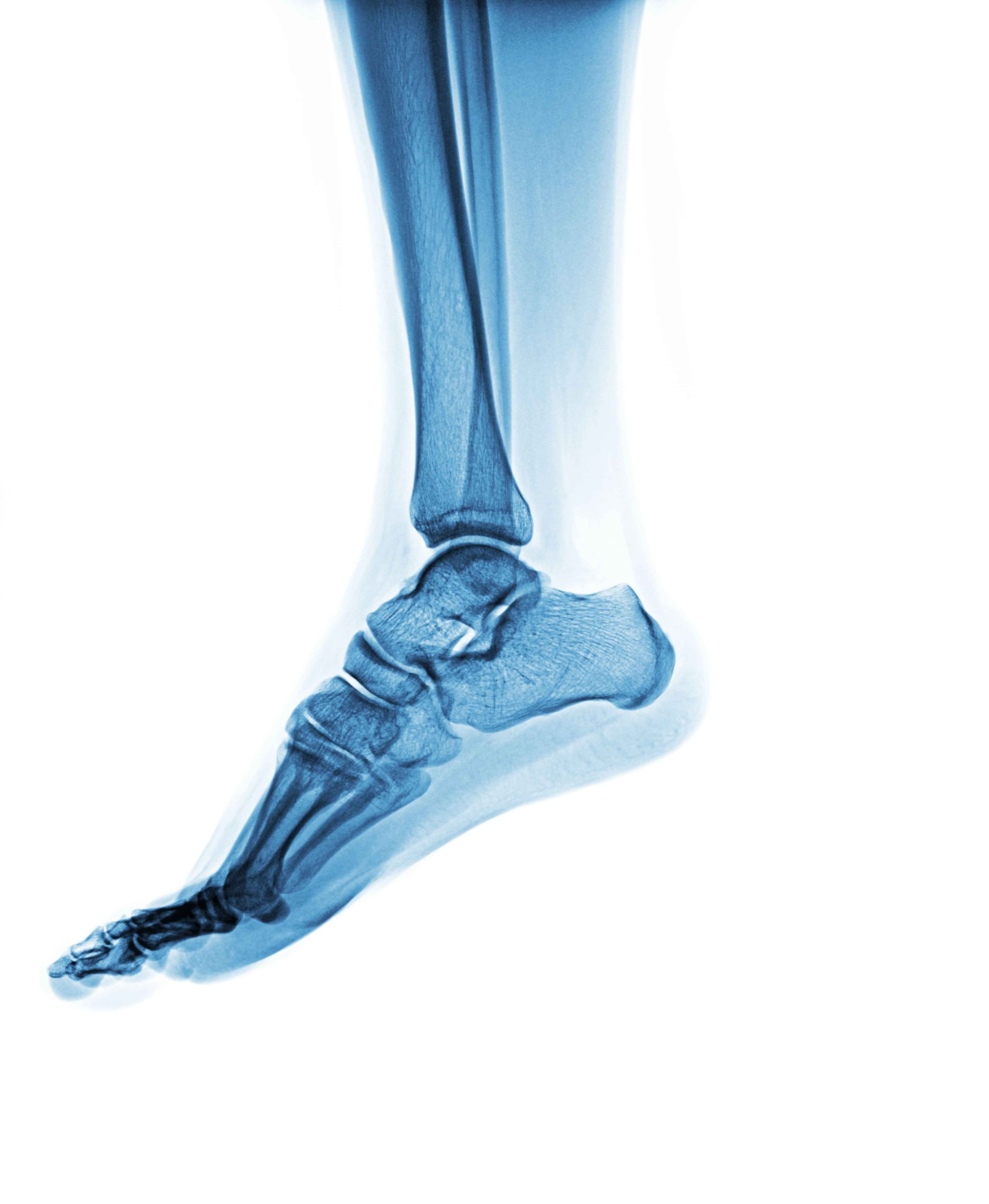
Diagnosing heel spurs usually involves a thorough examination by a healthcare provider. Imaging tests like X-rays might reveal the presence of a heel spur. However, it's essential to note that heel spurs might not always be the primary cause of heel pain; sometimes, symptoms might be due to plantar fasciitis or other conditions. Therefore, differentiating between heel spurs and other causes of heel pain requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional.
What treatments or strategies are effective in managing heel spurs?
Treatment for heel spurs generally focuses on alleviating pain and reducing inflammation. Conservative treatments include rest, ice application, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive footwear with proper arch support and cushioning. Orthotic inserts or heel pads may help distribute pressure more evenly and reduce discomfort. Stretching exercises targeting the calf muscles and the plantar fascia can also aid in managing symptoms. Physical therapy modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation might be utilized to provide pain relief.
In more severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments, medical interventions such as corticosteroid injections might be considered to reduce inflammation and pain. However, surgical options to remove the heel spur are rarely necessary and typically considered as a last resort if conservative methods fail to provide relief.

Are there lifestyle modifications or preventive measures to alleviate heel spur discomfort?
Lifestyle modifications focus on reducing activities that exacerbate heel pain, such as excessive walking or running on hard surfaces. Wearing appropriate footwear with good arch support and cushioning, avoiding high-impact activities, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce strain on the heel and the plantar fascia, consequently alleviating discomfort associated with heel spurs.

