Achilles Tendinopathy
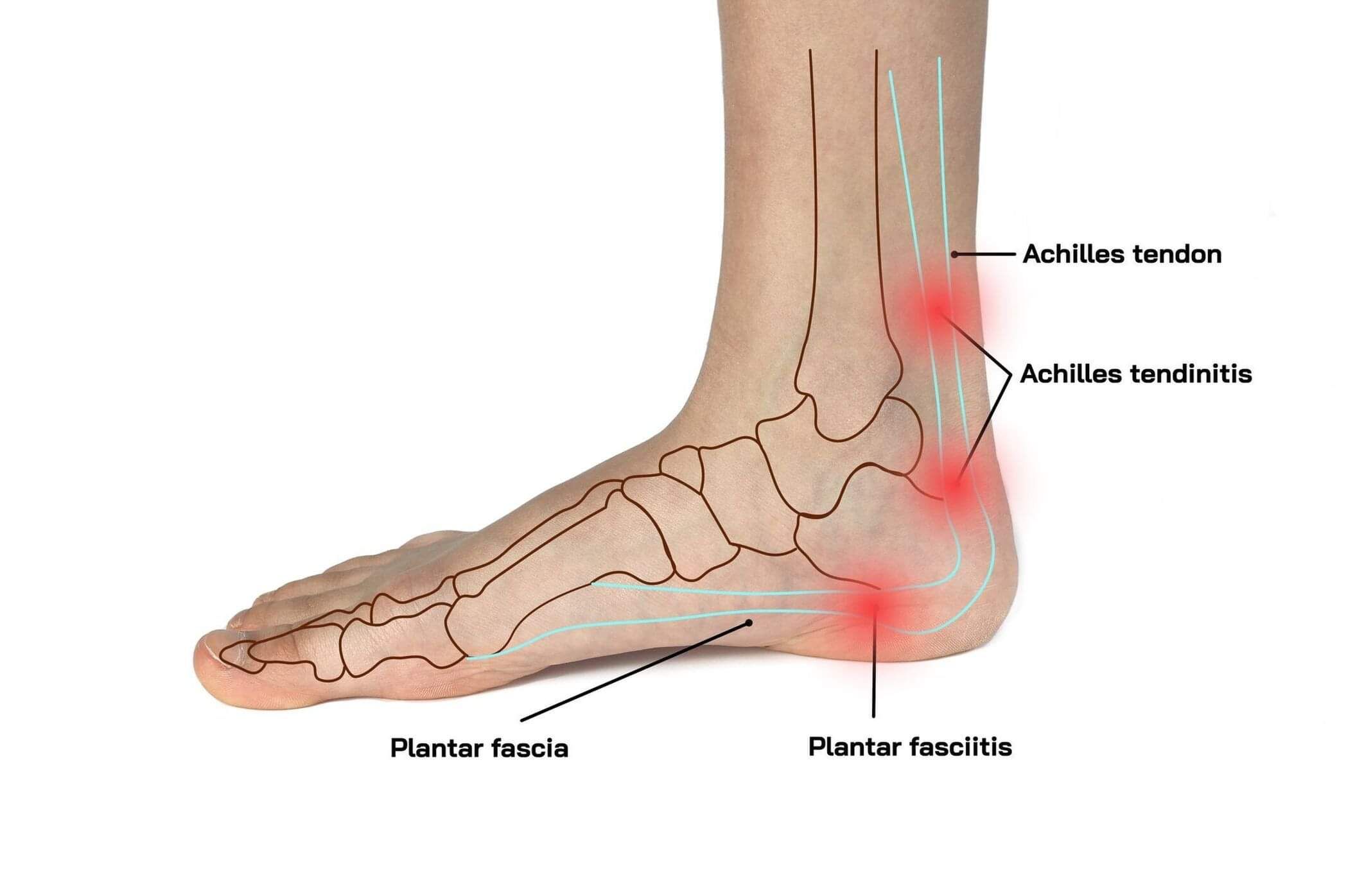
What is Achilles tendinopathy, and what are its symptoms?
Achilles tendinopathy refers to conditions affecting the Achilles tendon, the large tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition encompasses both Achilles tendinitis (inflammation of the tendon) and Achilles tendinosis (degeneration of the tendon without significant inflammation). Symptoms commonly include pain and stiffness in the Achilles tendon, particularly near the heel. The pain might worsen during physical activity and ease with rest, but in severe cases, it can become chronic and impact daily activities.
Individuals might experience tenderness, swelling, or a noticeable thickening of the Achilles tendon along with pain.
What are the common causes or risk factors for developing Achilles tendinopathy?
Achilles tendinopathy often develops due to repetitive stress or overuse of the Achilles tendon. Engaging in activities that involve sudden bursts of activity or continuous stress on the tendon, such as running, jumping, or certain sports like basketball or tennis, can contribute to the condition.
Other risk factors include sudden increases in physical activity intensity or duration, inadequate warm-up exercises, tight calf muscles, improper footwear, and biomechanical issues affecting the lower extremities.
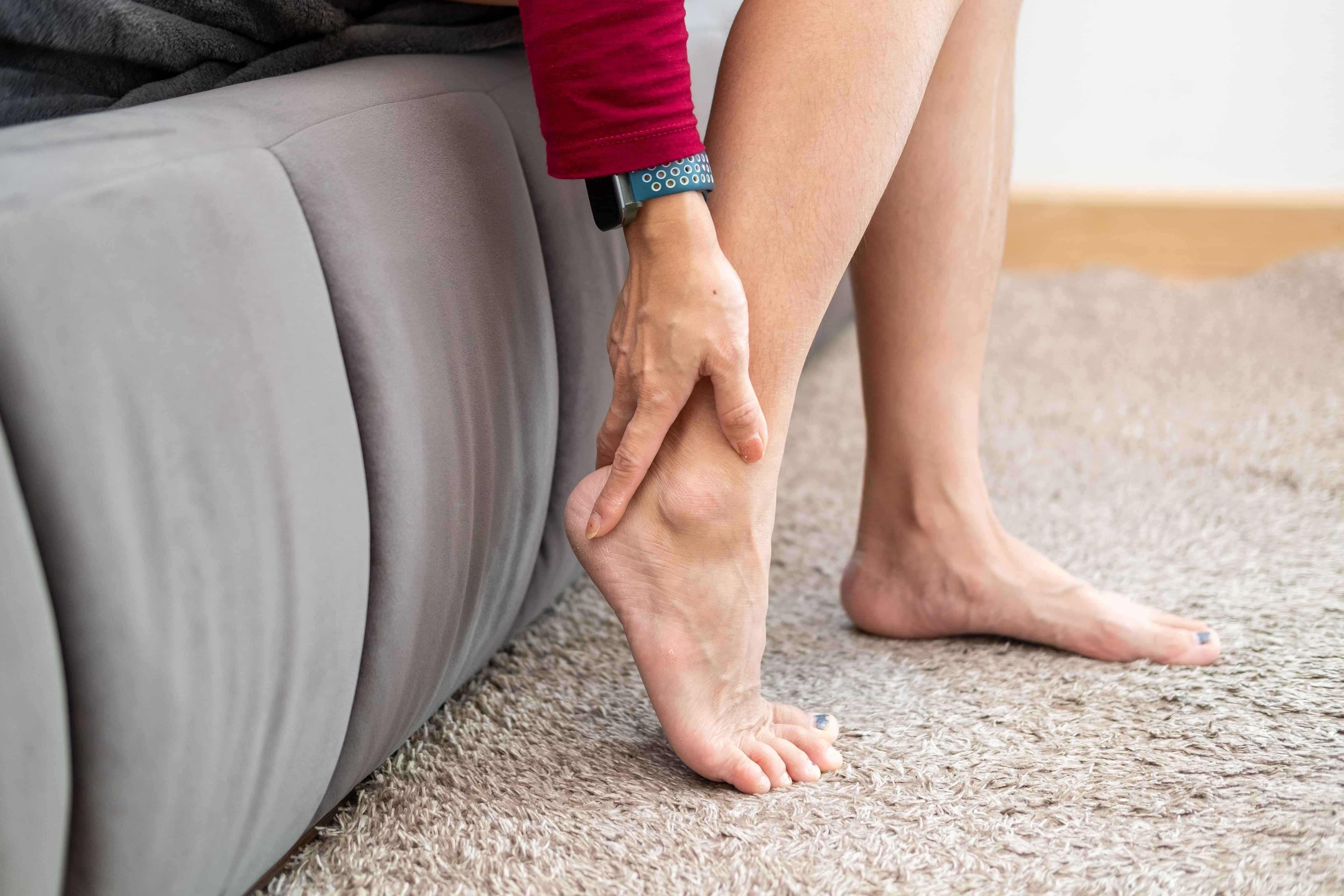

How is Achilles tendinopathy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Achilles tendinopathy involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. This includes a detailed assessment of the individual's medical history, symptoms, and a physical examination focusing on the Achilles tendon's tenderness and functionality.
Imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI scans may be recommended to visualize the extent of tendon damage, ruling out other potential causes of heel pain or identifying structural abnormalities.
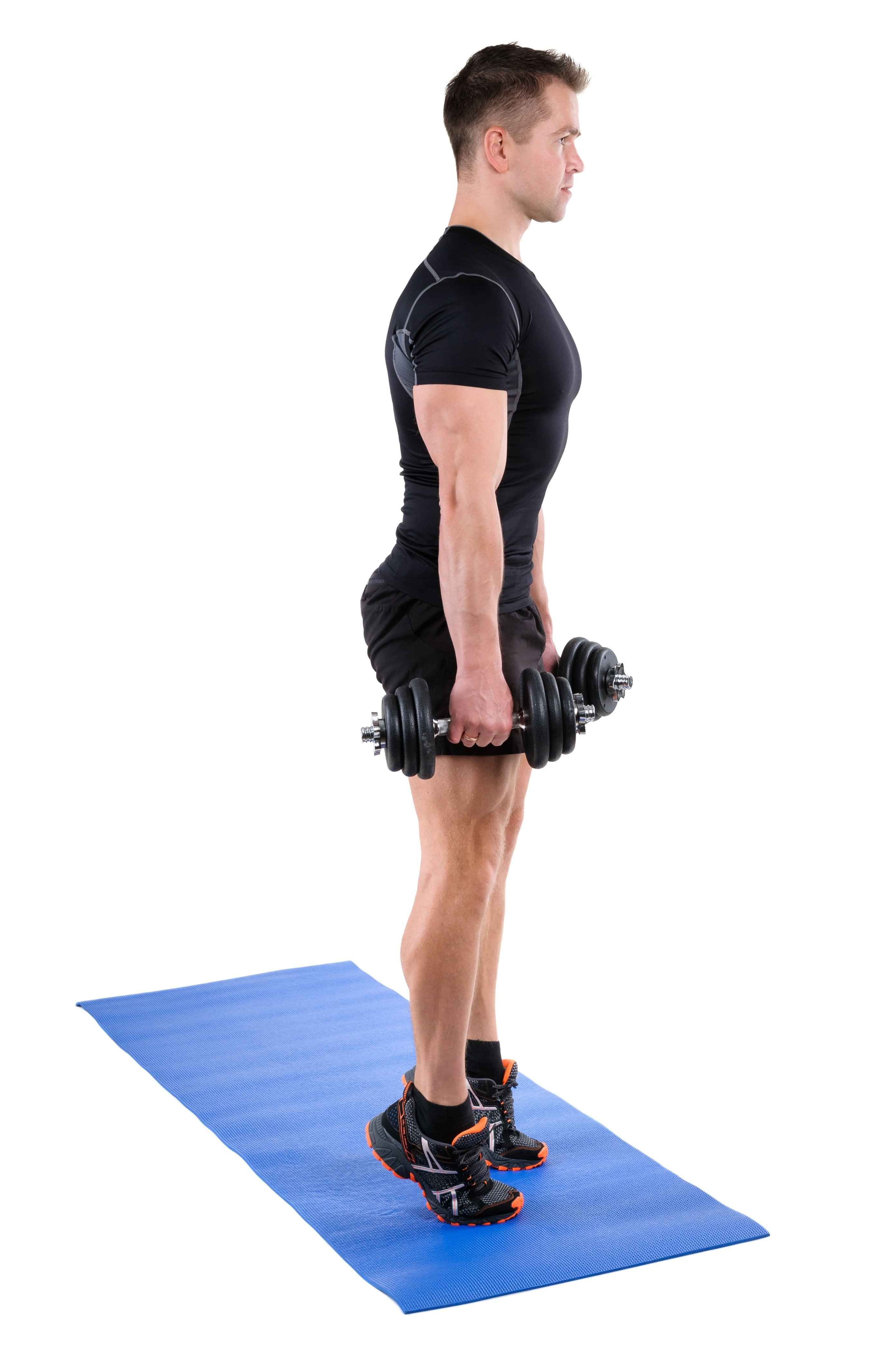

What are effective treatment options for Achilles tendinopathy?
Initial treatment for Achilles tendinopathy involves conservative measures aimed at reducing pain and inflammation. Resting the affected leg, applying ice to the area, and using over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help alleviate symptoms.
Physical therapy focusing on stretching and strengthening exercises for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can aid in recovery and prevent further injury. Eccentric strengthening exercises have shown effectiveness in treating Achilles tendinopathy.
Orthotic devices, such as heel lifts or custom orthotics, can provide support and correct any biomechanical issues contributing to the condition. In some cases, medical interventions like corticosteroid injections or extracorporeal shockwave therapy may be considered to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
For chronic or severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options such as tendon repair or debridement might be recommended.
Are there preventive measures or lifestyle changes to manage or avoid Achilles tendinopathy?
Preventive measures involve gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities to prevent overuse injuries. Ensuring proper warm-up and cooldown exercises before and after workouts or sports activities can reduce the risk of tendon injuries.
Wearing appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning for the feet and avoiding sudden changes in training routines can also contribute to preventing Achilles tendinopathy. Additionally, regular stretching exercises for the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Individuals should listen to their bodies and take adequate rest between activities to allow for recovery, particularly after strenuous exercises or prolonged physical activities. Maintaining overall lower extremity strength and flexibility through regular exercise and conditioning can help reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendinopathy.
Seeking professional advice and guidance from a healthcare provider or a physical therapist for proper training techniques and appropriate exercises can also be beneficial in preventing Achilles tendon injuries.

